



As countries across the globe aim to improve their development index in terms of economic and sociologicalparameters, it is desirable that focused development projects are completed successfully. World bodieslike the UNDP, World Bank, Asia Development Bank etc lay down budgets to fund such projects. However, itis seen that many of these projects turn out as failures or abandoned. Such instances are more pronouncedin countries from developing economies.
Report from the Abandoned Projects Audit Commission in 2011 listed that 11,886 federal government projects were abandoned between 1971 to 2011 in Nigeria, causing loss of billions of dollars. Similar reports have made headlines in other African countries too. In 2018, there were reports of a Power Plant in Jharkhand in India left abandoned, where State Bank of India had lent $700 Million. Similar occurrences of abandoned cities, dams, etc, are found across the globe. Unfortunately, apart from the economic losses, these also indicate loss of opportunity to achieve social milestones like poverty alleviation, employment opportunities, better standards of living, and thence, holistic development of the nation’s human resources.
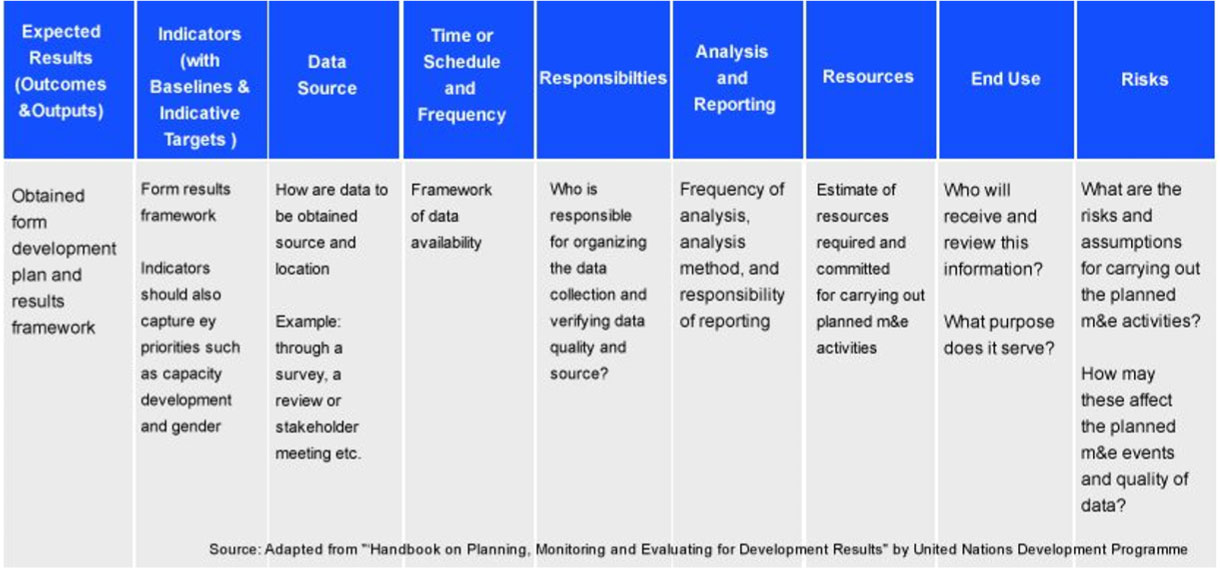
Most of these failures are attributed to a lack of continuum in planning, monitoring & evaluation of these projects. While there are established frameworks to achieve the same through matrix of indicators and activities, yet such projects suffer badly due to lack of visibility across the entire spectrum. While a lot of secretarial effort in invested in collecting information, collating the same and building linkages is a huge challenge. Such gaps therefore lead to leakages, unforeseen risks, and thereafter failure of the project to achieve its intended goals.
It is hence desirable that such large projects should be available to all stakeholders – planners,
monitors, evaluators & beneficiaries – for a continuous assessment and mid term correctives. It is
important that ICT are leveraged to achieve the same.
It is hence desirable that such large projects should be available to all stakeholders – planners,
monitors, evaluators & beneficiaries – for a continuous assessment and mid term correctives. It is
important that ICT are leveraged to achieve the same.
IDEA Foundation has developeds a web based solution at Datanalytics.online addressing all the above criteria. The project is scalable and can be used for small, medium or mega projects. An android application specifically designed for field staff and surveyors has also been developed. The application offers complete insulation and confidentiality to the subscribers as they access their own applications through independent subdomains. Each subscriber can manage more than one project with shared or independent teams. Graphical interfaces allow a quick visual report of the various aspects of the projects. Missed deadlines, failing indicators are suitably flagged. The application is designed in consultation with M&E experts. The design is a result of thorough study of the various manuals and handbooks of leading organizations like UNDP, WB, ADB etc.
Overall, a solution that allows panoramic view of multiple projects enabling planners, monitors and evaluators to connect with each other real time.
This blog is authored by Rajneesh Malviya, CEO, IDEA Foundation